The HIV virus is one
of the leading causes of death in our world today, with 50,000 new cases developing
per year. As HIV is much more common in poverty-stricken countries, my knowledge
of its existence only began in middle school, through television programs and
news articles. I’d assume that the case is the same for many Americans, as less
than 1% of our population is infected by the HIV virus.
Upon first learning of the virus a few years ago, I was
shocked to hear that there was no vaccine or treatment to rid a person of HIV.
I had erroneously thought that with the technology we have today, scientists
would have surely found a way to cure such a widespread disease. If the human
race has the ability to send a man to the moon and back, shouldn’t we be able
to mix up a concoction that kills a predator a million times smaller than the
tip of a needle?
As we learned in biology class this past week, creating a
vaccine or successful treatment for HIV is definitely not as simple as “mixing
up a concoction”. The contraction of diseases is different in every case, so HIV
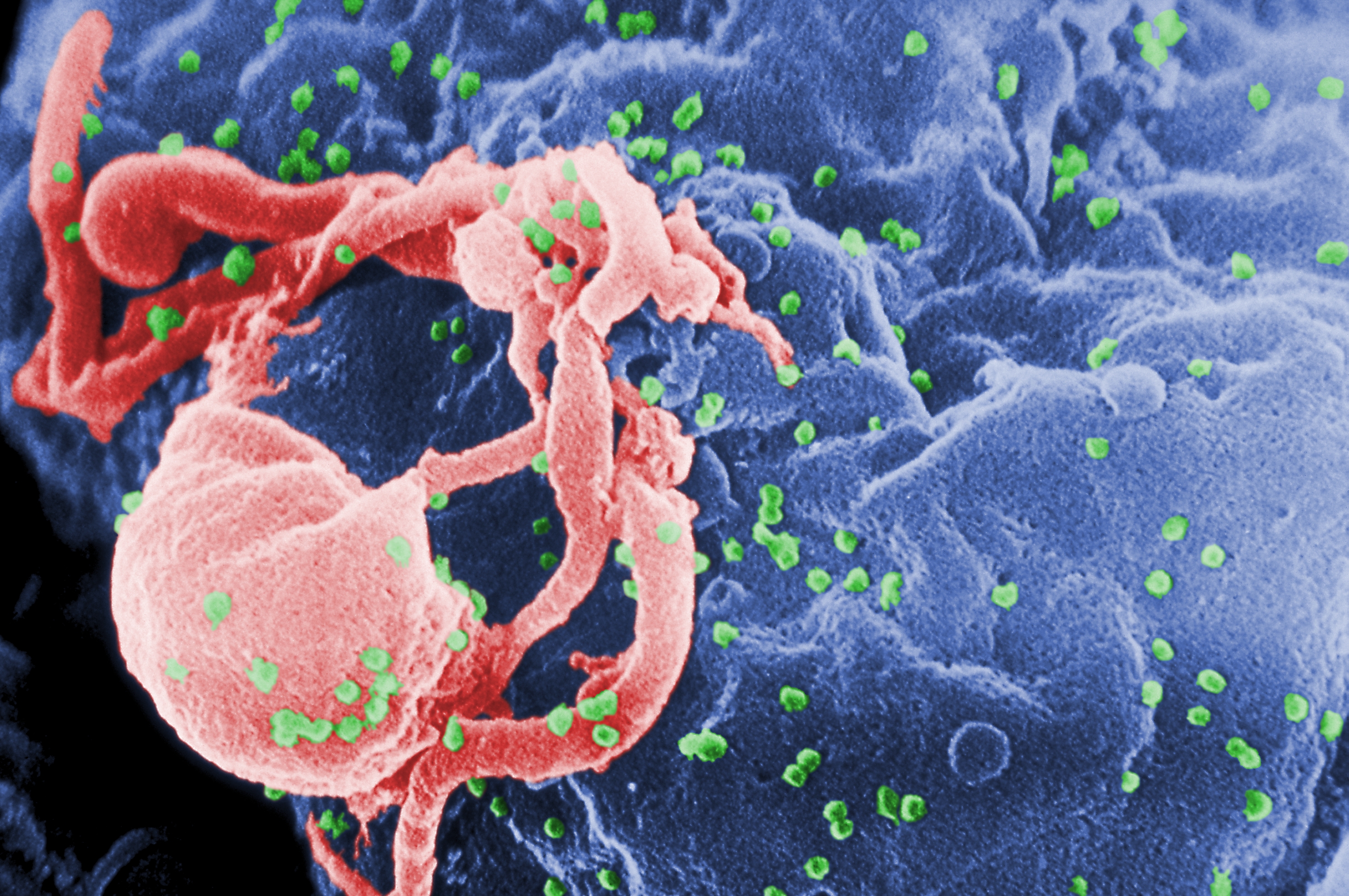
is sadly not as preventable as diseases like the flu. The HIV virus is spread
when certain bodily fluids of an infected person, such as blood, enter the
body. When the virus enters the blood stream it attaches to two white blood
cell receptors, first the CD4 and then the CCR5. The virus membrane then fuses
with the cell membrane, and attacks the white blood cell, eventually rendering
it useless to fight off diseases.
As we learned in our blood typing unit, everyone’s blood
cells are different, and the receptors and markers they have greatly contrast
with those of others’. When investigating the blood cells of those that are
unaffected by HIV, it has been found that they lack CCR5 receptors, preventing
the virus from attaching to the red blood cells. The first thing that comes to
mind when thinking about a way to treat and prevent HIV after hearing this is
to eliminate the receptors. If some people can survive without them shouldn’t
that be the case for everyone else? This is true, but removing eliminating a
receptor certainly isn’t an easy job.
How can the receptors be removed? This long-asked question
is finally being answered by Carl
June and Pablo Tebas, immunologists at the University of Pennsylvania in
Philadelphia. Their answer: Gene editing by way of enzymes. I learned of
this discovery by reading an article titled “Gene-editing Method Tackles HIV in
First Clinical Test” in the news section of the Nature Publishing Group
website, (URL “Nature.com”). The article was published on the 5th of
March 2014, written by Sara Reardon. The
article can be accessed by following this
link: http://www.nature.com/news/gene-editing-method-tackles-hiv-in-first-clinical-test-1.14813
Researchers
working with June and Tebas are using enzymes called zinc-finger nucleases
(what a name!) to find and destroy the genes in the cultured immune cells of 12
people infected with HIV. The enzymes target genes responsible for the CCR5
receptor in a search and destroy mission, killing off the problem from the root.
The treatment was
successful in “about 25% of each participant’s cultured cells” writes Reardon, which were then transfused back into the blood
of the patient from which they came. Half of the patients stopped their normal
antiretroviral drug therapy, and their levels of virus and T cells, T cells
being the type of white blood cells infected.
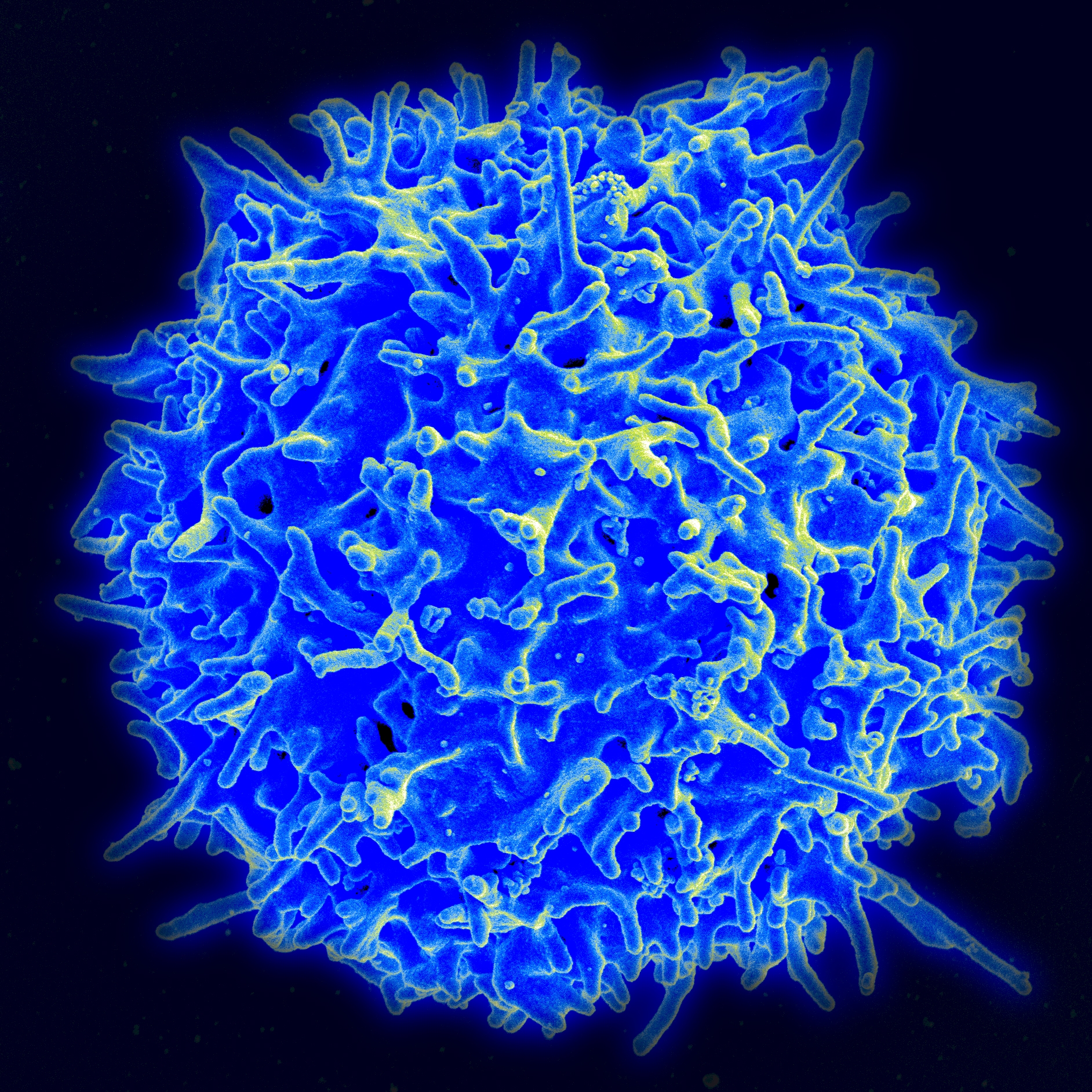
An image of a healthy T cell from a scanning electron microscope
The HIV levels rose more slowly
than they typically would without drug therapy, while the T cell count went up
and remained high for weeks.
This led
researchers to conclude that the presence of the virus drove the genetically modified
T cells to multiply and spread throughout the body in response.
“In short, the
presence of HIV seemed to drive the modified immune cells, which lacked a
functional CCR5 gene, to proliferate in the body.” says Reardon.
Researchers suspect that the virus was unable
to infect and destroy the altered cells.
In one of the
patients, the virus did not return at all over the twelve week period off of
antireviral drug therapy. Upon examination, the man was found to have already
had one non-working copy of CCR5. Quoting
Tebas, Reardon says that “Nature had done half of the job”.
This finding
suggests that others with one mutated copy of CCR5 would be perfect recipients
for the gene editing treatment. The team is currently enrolling people with
this trait in a new study, and are working on increasing the percentage of
modifiable cells and the rate at which the cells multiply in the body.
June, one of
immunologists responsible, says that he expects there to be even better enzymes
on the market in the near future, capable of targeting genes better than the zinc-finger
nucleases now are. He also thinks that enzyme based gene altering will be
available clinically in the not so far off future. These enzyme treatments are
not solely beneficial to curing HIV, but also certain other diseases.
“He expects researchers to start to look at
their potential for altering cells in people with disorders that result from
mutations in a single gene, such as sickle cell anaemia, certain types of
cancer and even metabolic diseases in the brain.”, Reardon writes of June.
This news is very
exciting to me, as June and Tebas’ discovery seems to be one of the most
genuine breakthroughs in HIV treatment that I have recently heard of. However,
it does seem like a very complicated treatment plan. Considering that the
countries with the highest percentages of HIV per population are those in Southern
Africa, a region known for its low income, I can’t help but think that the
treatment won’t be accessible to those who need it most if it is ever used
clinically. These transfusions and alterations aren’t the type of things that
can be done outside of sate of the art hospitals and laboratories, and they don’t
sound very cheap either.
I hope that the
gene alteration treatment of HIV is successful in years to come, but I still
worry about those who cannot access and afford it. Will healthcare cover the
costs? Do most of these people even have health care? I hope that when the time
comes for this treatment to be revealed, the cost of saving a life from the
slow death of HIV won’t be too much for those who need it.
Article Citation:
Reardon, Sara.
"Gene-editing Method Tackles HIV in First Clinical Test." Nature.com.
Nature Publishing Group, 5 Mar. 2014. Web. 20 Mar. 2014.
Picture Location:

Great Post Jessica! I found your post very well written and interesting. Your title was a great grabber because i found my self interested. I had no idea that to get in the HIV virus needed to use the CCR5 or that our genetics was fighting the HIV by removing its CCR5 receptors, but this might just be a temporary solution. Viruses will probably evolve a way to get into the cell without the CCR5 receptor, in this never ending war between us and viruses, but this discover bought us time. Over all I think this was a great post!
ReplyDeleteThis was a very good post. Your title caught my attention right away because it was a topic that we talked about in class. I liked the pictures you used in this post also because they were cool to look at and helped provide a visual of what you were explaining. I liked how you explained that our body's are learning to stop producing the CCR5 receptors so then can fight against the virus. Lastly I found it interesting that the cure could still possibly be used in low income areas like Africa were HIV is most common. I realy enjoyed reading your blog post and thought it was great!
ReplyDeleteJessica, this was a very interesting post. I like how what we went over in class has inspired lots of people in making blogs about cures for HIV or HIV Immunities. Like Cole said, I also liked how you included the fact that our bodies are learning to stop making the CCR-5 receptors. Great Job!
ReplyDeleteGreat Job! I liked you post and it was well written for such a long post. I liked how this ties in with what we did in class. I really liked how you put multiple pictures on your post. I also really liked how you mentioned where it was the worst and how it is the leading cause of death in the world. It left me thinking about HIV. Will it ever be cured? Overall, you did a great job so keep up the goo work!
ReplyDeleteThis is a fantastically written post! You really tied the subject into what we learned about in class, and your use of images really helped to capture the ideas talked about in this post. I liked that you didn't just focus in on how HIV affects Americans, and mentioned death rates world wide. I hope that a cure will soon be developed to battle against this horrible disease. Great job!
ReplyDeleteYou did a really nice job with this blogpost! There was alot of details and you accurately showed the scale of how HIV affects people all across the world. The pictures were a nice addition to your blogpost.
ReplyDeleteI really liked your blog! It was filled with specific details, which made the reading very easy. I loved the picture of the T cell and it supports your blog very nicely. I thought it was interesting how you focused the topic worldwide. Not many people have done that. It helps show how much HIV affects the world we live in today .Overall, awesome job!
ReplyDelete